Climatic chambers for standard Ford CETP:00.00-L-467 Ford Laboratory Accelerated Cyclic Corrosion Test
This standard specifies an accelerated laboratory atmosphere corrosion test. The testing environment addressed is similar in effect to that of the salt load/ climatic part of the proving ground corrosion test procedure, CETP 00.00-R-343 and yields corresponding results.
The objective of the test is to allow evaluation of the corrosion resistance of metals in environments where there is a significant influence of chloride ions, mainly as sodium chloride from a marine source or by winter road deicing salt.
This standard need a climatic chamber--salt spray test chamber.
The laboratory test provides full exposure to the salt load and humidity environment. It does not attempt to simulate other engraving factors such as mud loads, temperature stresses or wear. It serves as a general purpose atmospheric corrosion test and applies to a variety of materials, coatings, and interactions of materials, both as test specimens or in designed components.
The test can be used as a design verification method in order to develop and qualify new corrosion resistance products, develop new pre-treatments and finishing processes, select materials and perform quality control of the final product.
The standard specifies controlled conditions for equipment and procedures to allow the test to be preformed with a high degree of repeatability and reproducibility. It is designed to be suitable to run in various climate chambers, either as a fully automated procedure or with partial manual operations.
The workday test procedure consists of :
1. A 6h wet phase at room temperature with intermittent exposure to salt solution(0.5%NaCl).
2. A 2.5h transition phase with drying under climate control.
3. A 15.5h phase with constant temperature and humidity(50℃, 70%RH).
After repeating this procedure Mon-Fri a 48h weekend phase under continued constant climate control is added.
This is a control test and can be used to qualify components throughout the world. The test may be conduced at any location having the necessary equipment and facilities. Proposed revisions to this procedure must be submitted per FAP03-179.
The following elements are usually required to conduct the test procedure:
1. Compressed, clean air of 4-6 bars for cleaning salt solution from spray nozzles, as a source for the renewal of chamber air and for humidification, supplied by spray humidifiers.
2. A low conductivity water supply(20µS max) for humidification or evaporative spray humidifiers and for the preparation of salt solutions.
3. A tank for preparation and storage of salt solution or, alternatively, a system for direct on-line mixing of water and saturated NaCl solution to the actual concentration(0.5±0.05% by weight).
4. A conductivity meter with built-in temperature compensation for preparation and control of the 0.5% NaCl salt solution(conductivity: 8.3mS/cm±0.80 at 20℃). A 0.50% by weight NaCl solution is used as a calibration standard at each measurement.
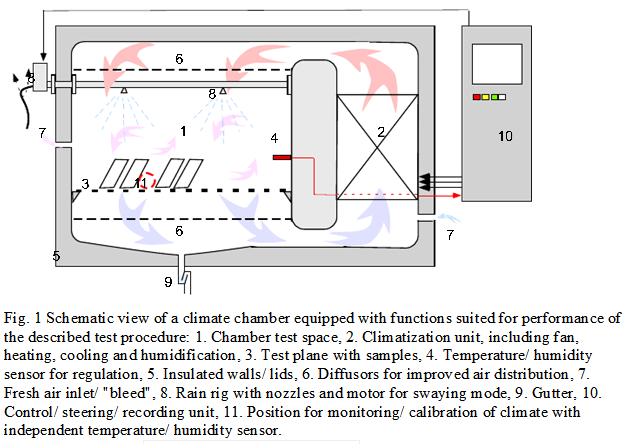
5. A high quality device for independent control of temperature and relative humidity shall be accessible. This instrument shall on a stipulated regular interval be used for independent monitoring and calibration of the conditions in the very test plane of the exposure chamber. The total measurement error must not exceed 0.1℃.
6. Racks of inert material for support and aligned fixation of test specimens must not hamper a free air-flow around the test objects, nor collect standing wetness. The test objects in a rack must not screen one another from the salt solution downfall and they should be exposed with the stipulated exposure angle to the spray(15-20 degrees inclination from vertical).
7. Pressurized hand-spray equipment for application of the 0.5% NaCl solution if a manual spray procedure is used. The capacity must be sufficient to meet the downfall requirements.
8. Funnels, beakersmeasuring glasses and a balance with at least 0.1g accuracy for monitoring and calibration of salt solution downfall throughout the test plane of the exposure chamber.
9. All the test measurement equipment must be calibrated and maintained per FAP03-015, Control, Calibration, and Maintenance of Measurement and Test Equipment.
10. All applicable safety guidelines and procedures must be followed.

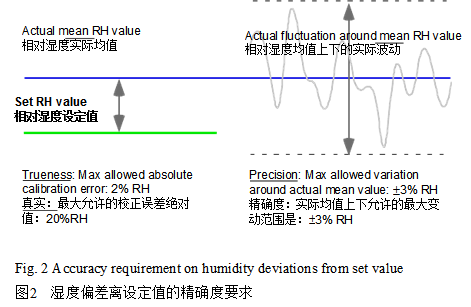
The maximum allowed short-term fluctuation in relative humidity overlaid on the calibrated mean value is ±3%RH, which implies a maximum allowed short-term temperature fluctuation of ±0.6℃. Figure 2 is exemplifying the requirements on relative humidity.
The chamber controlling software/ hardware must be designed so that the relative humidity may be changed linearly with time as depicted in the illustrated conditions, see figure 5. In the 2-stage ramping from a wet chamber at 25±2℃ to humid conditions at 50℃, 70%RH, the first heating stage to 40℃ should be reached within 30 minutes without sample drying, which is secured by a nominal relative humidity setting to 95%RH. The second 2h ramp must reach the stipulated final 50℃, 70%RH at the end of the ramp.
Note: For each new exposure situation this condition must be verified by an independent monitoring device with the sensor positioned among the actual test objects in their actual average plane of exposure. For monitoring: Deploy the sensor directly after the last spray event of the work-day wet phase.
In automated testing, forced cooling is necessary when proceeding from 50℃, 70%RH controlled, constant conditions to macro-wet conditions at 25℃. The chamber must achieve a cooling from 50℃ to 30℃ within 30 minutes with the targeted 25℃ met within 1 hour.
If spraying is applied manually, then cooling the samples by letting the chamber be open with test objects kept wet may provide an option that does not require the use of a built-in cooling unit. It must be verified by temperature monitoring that cooling requirements are fulfilled under such conditions for the actual chamber type and test specimen load.
For more details, please feel free to contact sales@lenpure.com
Please visit www.lenpure.com











